Evolution Mobile Technology: From 1G to 5G & Beyond Mobile technology
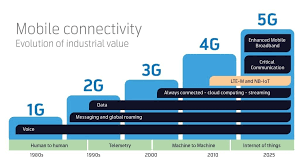
Beginning with the first generation of Mobile Communications that was an analog system, the second generation of digital system, the third generation of up to 2Mbps, the fourth generation of up to 100Mbps, and the fifth generation of up to 20Gbps, associated with low latency, each generation have made advancement features in connectivity. This moves into an era where 5G is now considered as a normalcy and the discourses are now about 6G and other subsequent mobile networks. This article aims to present information about mobile technology and its development with references to some aspects of 1G to 5G with focus on the further possible development.
1G: The Birth of Mobile Communication (1980s):
Mobile communication technology can be classified into five generations where the first generation of mobile technology, 1G for short, was developed in early 1980s, which is considered as the dawn of wireless communication. 1G networks were evolved on analog signals and mainly it was designed for conveyance of voice information. Although offering innovation solutions at the time it was developed, 1G technology had some drawbacks. Voice quality consisted poor quality in networks, had least capability, and no privacy thereby making calls easily vulnerable to tapping. Furthermore, 1G devices were also bulky, costly and used lot of power hence most people could not afford to own them.
Nevertheless, in regards to its achievement, 1G paved the way to future mobile technologies as it showed that mass scale wireless communications was possible. The first known 1G network was the Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) which was mainly used in United States but was adopted in other countries as well.

2G: The Shift to Digital (1990s):
The progress that was made in the field of mobile technology was carried in the second generation or 2G in the 1990s. More specifically, the 2G networks worked with digital signals in contrast with analog ones and this led to higher voice quality, more channel capacity and possibility to encrypt all the transmitted signals. The most popular 2G technology was the GSM or the global system for mobile communications that paved the way for the standard mobile networks around the world.
Text Messaging (SMS): SMS enabled users to send mobile messages from one mobile device to another: Short Message Service (SMS) therefore fostered the personal mobile communication evolution and crushed the initial entry opportunity to mobile data services.
Multimedia Messaging (MMS): Instead of plain text, it would be possible to send picture messages, voice and video messages.
Roaming: The 2G networks came with the features of international roaming which enabled the users to use the mobile services while in the foreign countries.
One major aspect of 2G was the mobile phones which became comparatively popular among public due to the reduction in size as well the lifespan of batteries present in the phones.

3G: The Mobile Internet Revolution (2000s):
3G or the third generation technology was brought about in early of 2000s to give you internet using your mobile phone. On the other hand, 3G was used mainly to sort data services along with a very basics one but it enabled users to get access to internet browsing, e mailing, etc. and to stream their multimedia on their mobile devices.
The 3G networks provided with data rates from 200 kbps to over 2 Mbps depending upon the 3G technology being used. Continued improvements in data functionalities were then seen in the introduction of WCDMA and HSPA which ensured that the mobile devices becoming more versatile.

Key features of 3G included:Key features of 3G included:
Mobile Internet Access: Users could surf the web, watch videos on the internet and download different applications which in turn marked the beginning of the invention of smartphones.
Video Calling: This also marked the first time that users could make video calls over the mobile networks only.
Improved Network Capacity: In terms of technology, 3G could allow for higher numbers of subscribers as well as devices to be connected at the same time; this would be instrumental in supporting the increase in demand of mobile services.
The extensive use of 3G was a turning point that paved way to the smartphone, mobile application, and the digital economy because it provided the convenience of mobile internet.
4G: High-Speed Connectivity and the Rise of Apps (2010s):
The 4G also called the fourth generation of mobile broadband technology that came into the market around early 2010s was more advanced as compared to the 3G regime. LTE emerged as the standard of the 4G offering and potential of data speed in excess of 100 Mbps. This in turn created a new phase of mobile advancements especially in the advancement of applications and consumption of content through mobile devices.
Key advancements with 4G technology included:Key advancements with 4G technology included:
High-Speed Data: 4G LTE network enabled users to stream videos, play online games and even download large files without lags.
Mobile Apps: The emergence of the app ecosystem with apple app store and google play store let the users to enjoy plethora of services from social media to banking right in their hand held devices.
Video Streaming: Some of the examples are Netflix, YouTube and Twitch, which benefited from 4G because they enabled people to watch videos on the move without interruptions.
Mobile Commerce: Mobile commerce experienced growth with the growth in connection speeds and frequency and people starting to engage in buying services, making financial transactions or renting products using their phones.
In addition, 4G grossed the enhancement of cloud computing because users could easily have faster data speed to access cloud services and store their data.
5G: The Era of Ultra-Fast, Low-Latency Connectivity (2020s):
Mobile technology finds a new era in the 2020s with the introduction of 5G, which has a step jump in both, speed and possibilities. 5G network technology is believed to offer download and upload speeds of up to 10 Gbps as well as latency of 1 ms at most. These low latency connections appear to create new opportunities in fields such as medicine, transport, entertainment and production in the sense of ultra fast.
Key features of 5G include:Key features of 5G include:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband: 5G provides through the option promising to be up to a hundred times faster than 4G; 5G facilitates streaming of 4K, 8K videos, virtual reality, and augmented reality experiences.
Internet of Things (IoT): 5G reach efficiently can cater the connecting devices that result from the IoT such as smart homes, wearables, automobiles, and industrial machinery.
Smart Cities: This will due to the fact that, 5G is slated to be instrumental in the establishment of smart cities where different systems in traffic flow, power and even safety will be well interconnected.
Autonomous Vehicles: Autonomous car functions require a low latency of 5G network to enable vehicles communicate with neighboring vehicles or traffic control systems, and provide processed instructions with cloud based artificial intelligence.
Telemedicine and Remote Surgery: Telemedicine in the 5G networks will allow doctors perform surgical operations remotely, and do video calls and data transfer in HD for health services to patients irrespective of the location they are in at that time required.

Beyond 5G: The Future of Mobile Technology:
That is why many researchers and industry pioneers have already started working on the development of 6G networks and further. Although still considered as the next generation beyond 5G only on the drawing board at present, 6G is projected to further increase the speed with some suggestions pointing to data rates up to as high as Tbps. Moreover, there is a possibility to have the even lower latency, the greater connectivity with a higher capacity and possible more energy efficient infrastructure of 6G networks.
Potential features of 6G and beyond include:Potential features of 6G and beyond include:
Holographic Communication: 7Real time communication with hologram of users that are at distant location; 6G networks may support fully controlled holographic communication.
Full Immersive Experiences: The 6G environment might create completely realistic Virtual and Augmented Reality that will affect industries such as the gaming industry, educational systems, and entertainment industries.
AI Integration: It also illustrates that the future mobile networks are expected to adopt AI rather deeply thereby making network operation more intelligent and self sufficient for traffic handling, resource allocation and service customization.
Conclusion:
Techno social change in context of mobility is from 1G to 5G, which now redefine the main social relations of mankind. Every generation offers a set of revolutionary improvements in connection, and thus, opens up possibilities for new applications and services which are impossible at the previous stage. With the further spreading of 5G all over the world, there are great perspectives for the utilization of mobile communications, 6G and further in terms of communication and advanced technologies. The trend in mobile technology will persist to be a leading force in the global advance of technology in most industries to the way we interact with the world.






3 thoughts on “The Evolution of Mobile Technology: From 1G to 5G and Beyond Mobile technology”