Introduction
It heralds the era of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in today’s technological world as a miracle solution for many areas of human life from health care to financing to daily life. This obvious fact does not make its usage any less frequent; however, mostly people do not understand the phenomenon of AI or consciously misinterpret it.
Understanding Artificial Intelligence
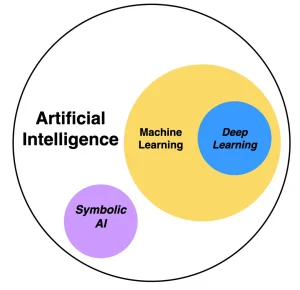
Artificial intelligence then becomes a branch of computer science that includes enhancing a system to performing operations based on a method normally employed by human intelligence ie, speech recognition, making decision and translation.
AI Two types:
Narrow AI: This type of AI is better called narrow AI, designed for a particular role. One of the applications include virtual personal assistants which include Amazon’s Alexa and Apple’s Siri and the recommendation systems of Netflix and Amazon, self driving cars, among others. This is to say that narrow AI cannot work outside (perform anything other than that) that its role has been programmed to do.
General AI: This subfield is also called strong AI or artificial general intelligence (AGI) its goal is to create an AI with the ability to learn and solve a multiple of problems similarly as a human would. Broad Artificial Intelligence is still on the drawing board and scientists have not developed this kind of Artificial Intelligence.
The History of AI
The history of AI began long before the invention of computers; the myths and legends of past years described automatons and artificial intelligence. Nevertheless, the scientific recognition of AI as a discipline was started in the twentieth century.
The Early Years
1950s: Alan Turing, a British mathematician, and logician developed the idea that there could be a machine that could mimic any human intelligence test. He proposed the Turing Test that would help him understand whether the machine was capable of, or had demonstrated human like intelligence.
1956: Alex Bernstein, John McCarthy, Marvin Minsky, Nathaniel Rochester, and Claude Shannon jointly formalized AI as a field organizing the first conference, ‘The Dartmouth Conference’. It is said that the term ‘artificial intelligence has been formed in this conference.
Key Concepts in AI
Machine Learning (ML):
ML can be categorized into three types:
Supervised Learning: In supervised learning the training data is labelled which implies that the inputs available to the algorithm are in conjunction with their correct result. Such cases are image classifiers and speech recognition systems.
Unsupervised Learning: The algorithm is then fed with such data and it has to search for patterns or indeed relations between the data inputs provided. Some are clustering or grouping in which objects are grouped based on their similarities or dissimilarities or events deemed anomalous by the system.
Reinforcement Learning: Machine learning process occurs when the algorithm engages with an environment and gets informed of the outcomes in the form of reward or punishment. Examples include, AI for playing games and robotic control.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is one of the branches of machine learning where neural networks with several layers are used and thus called deep learning. There are two characters routinely used in deep learning are convolutional neural networks and recurrent neural networks in speech and image recognition.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): It refers to creating mathematical models that let devices learn, translate, and produce natural languages. Some of applications that are implemented with this technology are; language translation, sentiment analysis, and chatbots.
Computer Vision
Computer vision is one of the subsets of artificial intelligence that makes the machines to understand and take the correct decisions on the world happenings from the vision. It is a field of study that deals with methods of obtaining, processing, analyzing, and comprehending images and Videos. Some of the uses are; Face identification; Self-driving cars; Examination of medical images.
Robotics:
Robotics is another subdivision of AI and is taken to as the science of making and using robots. Such machines are capable of operating automatically or semi-automatically; they also utilize artificial intelligence to move, pick, and decide. The applications are manufacturing, health care, and space exploration.
Ethical Considerations in AI
Applications of AI
Healthcare
AI is gradually turning into the healthcare model through which diseases are diagnosed, treatment advised and patient’s sicknesses managed. Applications include:
Medical Imaging: Here are some of the diseases that are diagnosed through medical images; cancer among them, have been diagnosed with better algorithms than radiologists.
Personalized Medicine: The type of treatment, which is expected to be the most effecting one, is determined by the use of AI algorithms, based on the patient’s genetic characteristics and past diseases.
Virtual Health Assistants: The other AI application is applied in chatbots and virtual assistants that provide health consultation services, schedule appointments, and monitor patients’ health.
Finance
The following is a discussion of roles of AI as pertains to the financial industry borrowing, fraud detection, trading, and customer service. Applications include:
Algorithmic Trading: Computerised high-speed programs employ market’s data and arrive at appropriate investment decisions.
Fraud Detection: ANN identifies exceptions in the transactional models put in to work that shell indicate fraudulent conducts.
Customer Service: Some of the tasks of chatbots include handling customer’s questions and concerns, and any financial and account-related inquiries.
Retail
AI is transforming the retail industry by bringing in accurate stock management, customers’ satisfaction, and enhancement of the supply chain processes. Applications include:
Recommendation Systems: Information of customers and their buying practices are then analyzed through the use of artificial intelligence to offer a relevant product.
Inventory Management: Actual sales, requirements and demand is predicted by the machine learning tools so that the problem of having too much stock or not having enough stock can be prevented.
Supply Chain Optimization: They are used in improving delivery time estimates as well as the appropriate routes to follow, and taking charge of delivery and warehousing facilities.
Autonomous Vehicles
Self-propelled transport like, self-driving automobiles, drones, etc are gradually observed to be supported by artificial intelligence. Contained in it are vision, sensors and learning algorithm by which the system is guided and makes the right choices. Applications include:
Self-Driving Cars: Modern novel self-driving systems are being piloted by Tesla and Waymo with the intention of getting through the most germane spaces of the urban environment.
Delivery Drones: Drones with the support of AI are used for delivery of parcel, providing medical necessity in several areas, and capturing and shooting.
Ethical Considerations and Challenges
The incorporation of AI has been expanding at a very high rate, and as a result, the following points of ethical concern have been identified.
Bias and Fairness:
AI systems can learn prejudices which are existent in the incipient data by mirroring and enhancing the prejudice when operating on larger data sets. That is why this can lead to unjust treatment of people in the areas of employment, credit, and policing. The principles mentioned above presuppose such approaches as the methods to identify and reduce bias and the formation of the diverse data datasets.
Privacy and Security:
One of the general issues in AI systems is voluminous data that need to be collected, which in turns poses privacy issues. The safeguard of the information with legal restrictions concerning data protection like the GDPR are also important. Thirdly, AI systems must consider threats of hacking and intrusions and other security breaches that are prominent in any socio-technical system.
Transparency and Accountability:
Various applications of AI have ‘black box’ characteristics, which raises the question of how decisions are arrived at. transparency means coming up with AI models which the user can understand how the end decision was arrived at. There is also the need to incorporate measures to address Accountable AI on the problems emerging from error or harm occasioned by the technology.
Job Displacement:
notably the Fordist jobs at the manufacturing floor, call center jobs and drivers of taxis. This is a challenge that calls for re-skilling and up-skilling of the workforce and formulation of policies that can be useful in re-deployment of workers.
Ethical AI Development:
Evaluating possibilities for building new AI systems according to the ethical standards means to have the consideration on the effect of developed systems on the society as a whole and the main idea about the AI’s positive impact on each participant of the process. These can be briefing on the principles of diversity and inclusion, the practice of human in the loop approach and practicing relevantethical principles in artificial intelligence research and development.
Conclusion
AI is a relatively young branch of science and technology which is constantly developing and could dramatically change some spheres of our existence. AI is already revolutionizing areas we rely on in our daily lives ranging from healthcare centre to the finance sector, education sector to transportation sector. But at the same time it opens up certain ethical and societal issues that need to be dealt with properly. Through cooperation, development of knowledge, and promotion of progressive rules, the possibility of AI’s benign impact on mankind can be achieved.







3 thoughts on “What is Artificial Intelligence to explain?”